“Decoding Thyroid Cancer: Understanding Thyroid Cancer Ultrasound Colors”
Introduction:
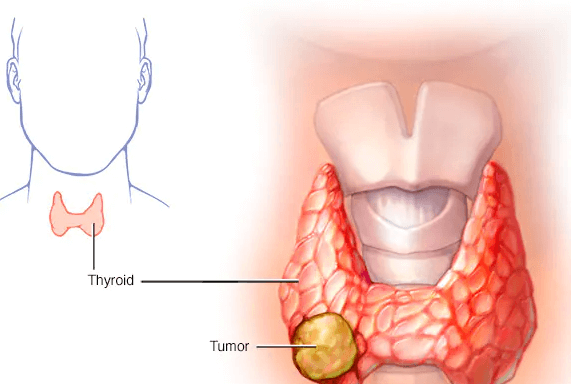
Thyroid cancer is a condition that affects the thyroid gland, a small but essential organ in the neck that regulates the body’s metabolism. Detecting and diagnosing thyroid cancer is crucial for timely treatment. Thyroid cancer ultrasound colors play a vital role in this process, providing valuable insights into the nature of thyroid nodules and helping medical professionals make informed decisions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the significance of thyroid cancer colors, and their interpretation, and answer frequently asked questions to demystify this important aspect of thyroid cancer diagnosis.
Thyroid Cancer Ultrasound Colors: What Are They?
Thyroid cancer ultrasound colors refer to the various shades and patterns displayed on ultrasound images of the thyroid gland. These colors are indicative of the tissue characteristics within the thyroid nodules and assist healthcare professionals in assessing the risk of thyroid cancer. Understanding these colors is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Read also https://mattbrogi.com/world-news/
Interpreting Thyroid Cancer Ultrasound Colors
- Hypoechoic (Dark Gray/Black):
- Hypoechoic nodules appear darker on ultrasound images.
- These nodules are often solid and can be concerning, as they may indicate an increased risk of thyroid cancer.
- Medical professionals typically recommend further evaluation for hypoechoic nodules.
- Isoechoic (Gray):
- Isoechoic nodules have a similar color to the surrounding thyroid tissue, making them challenging to distinguish.
- While they may be benign, they can still be cancerous, so close monitoring is essential.
- Hyperechoic (Light Gray/White):
- Hyperechoic nodules appear lighter on ultrasound images.
- They often contain more fat and are usually benign, posing a lower risk of thyroid cancer.
- Anechoic (Black):
- Anechoic nodules appear completely black and are usually filled with fluid.
- They are typically benign cysts and rarely cancerous.
- Mixed Patterns:
- Some nodules may exhibit mixed patterns, displaying characteristics of different colors.
- The interpretation of mixed patterns may require more detailed evaluation to determine the risk of thyroid cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- Q: What are the common symptoms of thyroid cancer?
A: Common symptoms may include a lump or swelling in the neck, changes in voice, difficulty swallowing, and persistent hoarseness. - Q: Are all thyroid nodules cancerous?
A: No, the majority of thyroid nodules are benign. Thyroid cancer is relatively rare, with only a small percentage of nodules turning out to be cancerous. - Q: How is thyroid cancer diagnosed and confirmed?
A: Thyroid cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of thyroid ultrasound, fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy, and possibly additional imaging tests. - Q: What is the role of a thyroid ultrasound in the diagnosis of thyroid cancer?
A: A thyroid ultrasound helps identify and assess thyroid nodules. It can determine the size, location, and characteristics of the nodules, aiding in the evaluation of their potential for malignancy. - Q: Can thyroid cancer be treated successfully?
A: Yes, when detected early, thyroid cancer is highly treatable. Treatment options may include surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and, in some cases, targeted therapy or chemotherapy.
Conclusion:
Understanding thyroid cancer ultrasound colors is a critical component of the diagnostic process for thyroid nodules. While the interpretation of these colors can provide valuable insights, it’s important to remember that a definitive diagnosis of thyroid cancer often requires additional testing, such as a fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy. If you have concerns about your thyroid health or have identified any thyroid nodules, consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate guidance on diagnosis and treatment. Early detection and prompt intervention can significantly improve the prognosis for individuals with thyroid cancer.